Compositions en R-JSON (JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS et ->>)
Exemple :
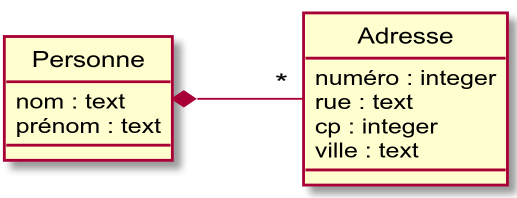
@startuml
hide circle
class Adresse {
numéro : integer
rue : text
cp : integer
ville : text
}
class Personne {
nom : text
prénom : text
}
Personne *- "*" Adresse : " "
@enduml
Exemple :
1
CREATE TABLE Personne (
2
sk TEXT PRIMARY KEY,3
nom TEXT NOT NULL,
4
prénom TEXT NOT NULL,
5
adresse JSON
6
);
1
INSERT INTO Personne
2
VALUES (3
1,4
'Holmes',5
'Sherlock',6
'[7
{"numéro":221,"rue":"rue du boulanger", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"},8
{"numéro":0,"rue":"rue Secrète", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"}9
]'10
);
11
12
INSERT INTO Personne
13
VALUES (14
2,15
'Watson',16
'John',17
'[18
{"numéro":221,"rue":"rue du boulanger", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"}19
]'20
);
1
sk | nom | prénom | adresse
2
----+--------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------
3
1 | Holmes | Sherlock | [ +
4
| | | {"numéro":221,"rue":"rue du boulanger", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"},+5
| | | {"numéro":0,"rue":"rue Secrète", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"} +6
| | | ]
7
2 | Watson | John | [ +
8
| | | {"numéro":221,"rue":"rue du boulanger", "cp":60200, "ville":"Compiègne"} +9
| | | ]
Syntaxe : Convertir un tableau d'objets JSON en relationnel : opérateurs JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS et ->>
1
SELECT a->>a1, a->>a2... FROM t, JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(t.jsonatt) a
Exemple :
1
SELECT p.nom, p.prénom, CAST(ad->>'numéro' AS INTEGER) AS numéro, ad->>'rue' AS rue, ad->>'ville' AS ville
2
FROM personne p, JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(p.adresse) ad
1
nom | prénom | numéro | rue | ville
2
--------+----------+--------+------------------+-----------
3
Holmes | Sherlock | 221 | rue du boulanger | Compiègne
4
Holmes | Sherlock | 0 | rue Secrète | Compiègne
5
Watson | John | 221 | rue du boulanger | Compiègne
Rappel :
Il est nécessaire d'utiliser la fonction CAST pour obtenir un type autre que chaîne de caractère.